Simulated Annealing¶
Simulated annealing contents¶
Simulated annealing introduction¶
Minimization by simulated annealing is performed by a modified version of the GSL algorithm in the anneal_gsl class. A version which includes OpenMP and MPI parallelization is provided in anneal_para.
Simulated annealing example¶
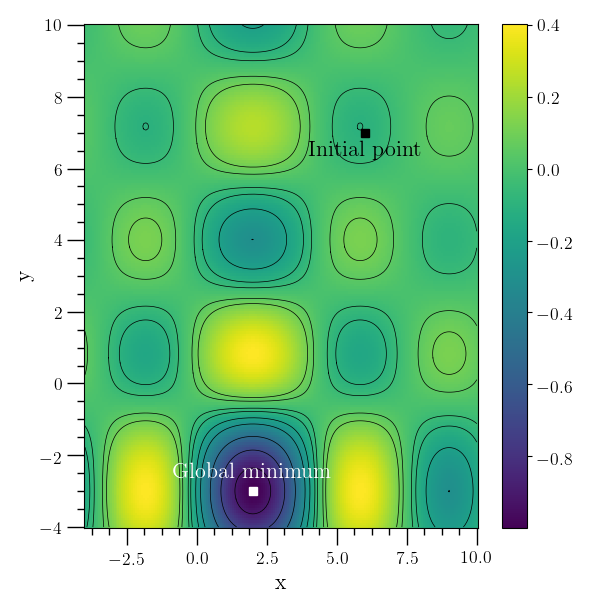
This example minimizes the function
\[f(x,y) = J_0(x-2) J_0(y+3)\]
over \((x,y)\) where \(J_0(x)\) is the Bessel function
given in gsl_sf_bessel_J0. The initial guess at \((9,9)\)
is far away from the global minimum.
The plot below plots the function above, the initial guess, and the minimum obtained by the example program.
/* Example: ex_anneal.cpp
-------------------------------------------------------------------
An example to demonstrate minimization by simulated annealing. See
"License Information" section of the documentation for license
information.
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <boost/numeric/ublas/vector.hpp>
#include <gsl/gsl_sf_bessel.h>
#include <o2scl/multi_funct.h>
#include <o2scl/funct.h>
#include <o2scl/anneal_gsl.h>
#include <o2scl/test_mgr.h>
#include <o2scl/hdf_file.h>
#include <o2scl/hdf_io.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace o2scl;
using namespace o2scl_hdf;
typedef boost::numeric::ublas::vector<double> ubvector;
// Make data for the plot in the documentation
void make_plot_data();
// A simple function with many local minima. A "greedy" minimizer
// would likely fail to find the correct minimum.
double bessel_fun(size_t nvar, const ubvector &x) {
double a, b;
a=(x[0]-2.0);
b=(x[1]+3.0);
// This is important to prevent the annealing algorithm to
// random walk to infinity since the product of Bessel
// functions is flat far from the origin
if (fabs(x[0])>10.0 || fabs(x[1])>10.0) return 10.0;
return -gsl_sf_bessel_J0(a)*gsl_sf_bessel_J0(b);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
cout.setf(ios::scientific);
test_mgr t;
t.set_output_level(1);
anneal_gsl<> ga;
double result;
ubvector init(2);
multi_funct fx=bessel_fun;
ga.ntrial=4000;
ga.verbose=1;
ga.tol_abs=1.0e-7;
ga.T_dec=1.1;
// Set a large initial step size
double step[1]={10.0};
ga.set_step(1,step);
// Choose an initial point at a local minimum away from
// the global minimum
init[0]=6.0;
init[1]=7.0;
// Perform the minimization
ga.mmin(2,init,result,fx);
cout << "x: " << init[0] << " " << init[1]
<< ", minimum function value: " << result << endl;
cout << endl;
// Test that it found the global minimum
t.test_rel(init[0],2.0,8.0e-2,"another test - value");
t.test_rel(init[1],-3.0,1.0e-2,"another test - value 2");
t.test_rel(result,-1.0,1.0e-3,"another test - min");
make_plot_data();
t.report();
return 0;
}
void make_plot_data() {
table3d t3d;
uniform_grid_end<double> ug(-4.0,10.0,199);
t3d.set_xy("x",ug,"y",ug);
t3d.new_slice("f");
for(size_t i=0;i<t3d.get_nx();i++) {
for(size_t j=0;j<t3d.get_ny();j++) {
ubvector v(2);
v[0]=ug[i];
v[1]=ug[j];
t3d.set(i,j,"f",bessel_fun(2,v));
}
}
hdf_file hf;
hf.open_or_create("ex_anneal_plot.o2");
hdf_output(hf,(const table3d &)t3d,"ex_anneal");
hf.close();
return;
}